Are you wondering about the AI pipeline workflow? Automation is the buzzword in the world of Artificial Intelligence. Businesses worldwide are desperate to build automation workflows to scale smartly. Developing practical pipeline workflows can revolutionize your costly business operations and set you up for success.
In this detailed blog, I will tell you everything you need to know about the AI Pipeline workflow and how to build smarter pipelines.
What Is an AI Pipeline Workflow?
An AI Pipeline Workflow is a structured process that takes data through steps like collection, preparation, model training, and deployment to produce intelligent results. It helps teams build, run, and manage AI systems in a clear, repeatable, and efficient way.
How is this different from AI automation? Well, the key difference is its purpose and depth.
AI automation focuses on automating tasks or decisions using AI (the outcome), while an AI pipeline workflow focuses on how AI systems are built, trained, updated, and maintained from start to finish (the process).
Imagine a coffee machine. Pressing a button and getting coffee automatically is AI automation. But designing the machine, choosing the beans, grinding them, brewing correctly, and maintaining the machine over time is the AI pipeline workflow. Without the workflow behind the scenes, the automation wouldn’t work or improve.
In real life, many teams can create an AI model that works in a test setup, but struggle to use it reliably in everyday business operations. The model might work once, but not consistently over time.
An AI pipeline workflow solves this by ensuring every step, from preparing data to using the model and updating it later, happens smoothly and repeatably. This helps AI systems work properly, scale with the business, and stay useful over time.
Struggling to find the perfect workflow automation tools? Discover the right tools here: 10 Ways to Automate Your Workflow with AI Tools
Stages of an AI Pipeline Workflow
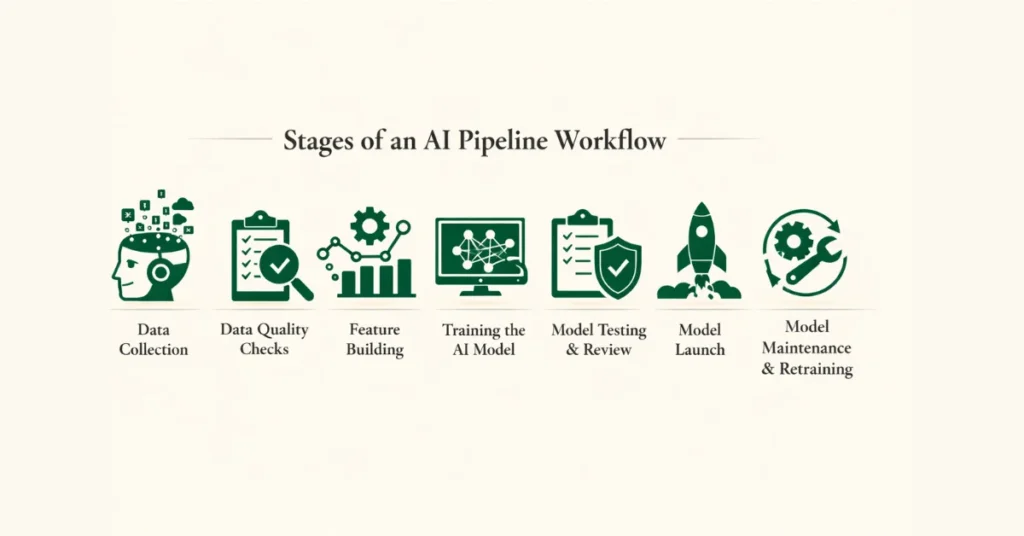
Even though the tools and setups may differ, most real-world AI pipelines follow a similar flow. Each step matters, and if one step is weak, it can cause problems later down the line.
Data Collection
Data collection is where everything starts in an AI pipeline. This is the step where you pull in raw data from different places and bring it into one safe, organized space so the next steps can work properly.
That data can come from many sources, like databases, live user events, cloud storage, SaaS tools, system logs, sensors, or outside APIs. A good ingestion setup can handle changes in data format, work with both scheduled batches and real-time streams, and make sure no data goes missing. Most experienced teams send all incoming data to a central place, like a data lake or warehouse, so everyone works from the same trusted data instead of juggling disconnected systems.
Data Quality Checks
Raw data almost never comes ready to use. It’s usually messy, incomplete, or broken in small ways that can quietly damage your whole system if you don’t fix it early.
This stage cleans things up. You check for missing values, fix messy formats, remove duplicates, filter out bad data, and apply privacy rules when needed. Most importantly, this process runs automatically. If the system spots too many problems, it can stop the AI pipeline workflow, notify your team, or send the data for manual review. Think of it like airport security for your data; it catches problems before they spread. This turns data quality from a “nice to have” into something you can actually rely on every day.
Feature Building
Feature building is where cleaned data turns into something an AI model can actually understand. You take raw values and shape them into useful signals, like turning clicks into user activity scores, labels into numbers, text into vectors, or past behavior into simple trends over time.
In real systems, teams do not create features randomly or on the fly. Instead, they use feature stores to keep feature definitions consistent and reusable. This makes sure the model sees the same inputs during training and when it runs in the real world. You can think of it like using the same measuring cup every time you cook; it keeps results predictable, reduces future cleanup work, and stops small differences from ruining your predictions.
Training the AI Model
The training stage is where the model actually learns. You feed it the prepared features and let it practice, usually by splitting the data, trying different model options, tuning settings, and saving the results.
Training does not always happen at random times. It can run on a schedule, start when enough new data arrives, or kick in when monitoring shows the model is getting worse. Teams also track and label every training result, so they can repeat experiments, understand past decisions, or go back to an older version if something breaks. It is like saving game checkpoints; you can always return to a safe spot instead of starting over.
Model Testing & Review
You do not get the license unless you pass all the driving tests. Before you release a model, you need to make sure it truly deserves to go live. This step checks how accurate the model is, how stable it behaves, whether it treats data fairly, and if it fits real business limits like cost or risk.
Many AI pipelines add approval checks at this point. If the model does not meet the rules you set, the system automatically stops it from moving forward. This way, good governance becomes part of the AI workflow itself, not something you try to fix after problems show up.
Model Launch
Deployment is the step where your approved model goes out into the real world and starts making predictions that actual systems use. Depending on the situation, the model might run on large batches of data, answer requests through an API, or process data streams in real time.
Behind the scenes, orchestration tools make sure the model works smoothly with incoming data and the applications that depend on its output. Speed, stability, and the ability to quickly undo changes matter a lot here. If deployment goes wrong, everyday business processes can break, just like a bad software update can crash an app people rely on.
Model Maintenance & Retraining
Once the model is live, the job is not over. At this point, the pipeline switches to constant watch mode. It keeps an eye on changes in incoming data, model accuracy, system health, and even costs.
When the numbers start to slip or the data begins to look different, the system can trigger retraining to fix the issue. This stage turns AI from a one time setup into something that grows and adjusts over time. Just like routine health checkups, they help catch problems early and keep everything running smoothly.
Stages of AI Pipeline at a Glance
| Stage | Purpose | Risks if Done Poorly |
| Data Collection | Bring raw data from different sources into one controlled place | Missing data, delayed updates, broken pipelines |
| Data Quality Checks | Clean, standardize, and verify data quality before use | Silent errors, bad predictions, compliance issues |
| Feature Building | Turn cleaned data into meaningful signals that the model can learn from | Inconsistent features, unreliable predictions |
| Model Training | Teach the model patterns using prepared features | Overfitting, poor accuracy, wasted compute |
| Model Testing | Check accuracy, fairness, stability, and business rules | Risky decisions, bias, failed audits |
| Model Launch | Make the model available for real-world predictions | System outages, slow responses, business disruption |
| Model Maintenance & Retraining | Track performance and update the model as data changes | Model decay, rising errors, lost trust |
How to Build an AI Workflow Pipeline Step by Step
Identify and Map Processes
Start by spotting tasks that happen often, follow clear rules, and use structured data, like approving invoices, updating a CRM, or scoring leads. These are the areas where AI can make the biggest impact quickly.
Pick the Right AI Models for Each Task
Choose models that match the job: classification models for sorting items, NLP models for understanding text, and regression models for predicting numbers. You can connect them together using APIs or no-code workflow tools.
Connect an AI Workflow Platform
Tools like Whalesync, Pega, or Appian help link your AI logic to business systems such as Slack, Salesforce, or HubSpot, so everything runs smoothly together.
Test, Track, and Improve
Start small with a pilot using a limited dataset. Keep an eye on results, tweak the workflow, and improve speed and accuracy before rolling it out widely.
Keep Governance and Compliance in Check
Make sure every AI-driven decision, especially in regulated fields like finance or healthcare, is explainable, logged, and auditable. This helps you stay compliant and build trust in your system.
AI Workflow Stages
| Stage | Purpose | Example Use Case |
| Data Ingestion | Gather data from multiple sources into one place | An online store collects customer clicks, orders, and product reviews |
| Data Preparation | Clean, standardize, and organize data for AI | The system removes duplicates, fixes missing addresses, and labels product categories |
| AI Modeling | Use AI to detect patterns and make predictions | The model predicts which products a customer is likely to buy next |
| Decision Making | Turn predictions into actionable steps | The system decides which customers should receive a special offer email |
| Action Execution | Apply AI-driven decisions in real-world systems | Automated emails are sent, and personalized discounts are added to customer accounts |
| Learning & Improvement | Monitor outcomes and retrain the model | The system adjusts future recommendations based on which offers were clicked or purchased |
Read Also: 10 Ways to Automate Your Workflow with AI Tools
Best Practices for Designing AI Pipeline Workflows
1. Start Simple and Build in Small Steps
Begin with a clear and simple pipeline. Focus on solving one problem well before adding more steps or complexity. Think of it like learning to ride a bike, you start steady before adding speed or tricks. A simple design makes it easier to debug, improve, and explain to others.
2. Automate Wherever Possible
Manual steps slow things down and increase the chance of mistakes. Automate data checks, model training, testing, and deployments so the pipeline can run smoothly on its own. This is like setting up automatic bill payments; once it works, you do not have to worry about it every time.
3. Keep Training and Production in Sync
Make sure the data and features used during training are the same ones used when the model runs live. Small differences can lead to wrong predictions later. Using shared tools and consistent definitions helps avoid surprises, much like using the same recipe every time you cook a favorite dish.
4. Monitor Everything That Matters
Always track model performance, data changes, system health, and costs after deployment. If something starts to drift, you want to know early. This is similar to checking your car dashboard while driving; warning lights help you fix problems before they get serious.
5. Design for Change from Day One
Data changes, user behavior shifts, and models age over time. Build your pipeline so retraining, updates, and rollbacks are easy to trigger. A flexible pipeline is like a good wardrobe; it adapts to different seasons without starting from scratch.
Why AI Pipeline Workflow Matters in 2026?
AI Models Are Easy, Reliability Is Not
In 2026, training an AI model is no longer the hard part. Almost anyone can build one. However, keeping that model reliable in real conditions is much harder. Data keeps changing, users behave differently, and small issues can slowly break performance.
Data Changes Faster Than Models
Meanwhile, real-world data never stays still. Customer habits shift, markets evolve, and new patterns appear constantly. As a result, models that once worked well can fail quietly. AI pipeline workflows catch these changes early and keep systems from drifting off course.
Pipelines Turn Experiments Into Systems
Because of this, pipelines matter more than ever. They replace one-off experiments with repeatable processes. Instead of guessing, you monitor data, test performance, and retrain automatically. This consistency is what allows AI to work every day, not just in demos.
AI Now Drives Real Business Decisions
At the same time, AI now sits inside critical workflows. It helps decide prices, approvals, recommendations, and risk. Therefore, mistakes cost real money and affect real people. Pipelines add structure, checks, and transparency so decisions stay controlled and explainable.
Scaling AI Without Losing Control
As AI adoption grows, companies run many models at once. Without pipelines, each one becomes a fragile setup. In contrast, standardized workflows make scaling possible. You reuse patterns, move faster, and avoid chaos, much like using assembly lines instead of building everything by hand.
Trust Is the New Competitive Advantage
Finally, trust has become a business requirement. Users and regulators want proof that AI systems are monitored and improved over time. A strong pipeline shows responsibility, not just innovation. In 2026 and beyond, that trust is what separates serious AI teams from the rest.
Key Benefits Across Industries
Marketing
In marketing, speed and accuracy matter a lot. An AI pipeline workflow helps teams collect customer data, clean it, and turn it into insights without manual effort. As a result, campaigns stay relevant even when user behavior changes quickly. You can personalize messages, test ideas faster, and avoid making decisions based on outdated data.
Finance
In finance, small errors can turn into big losses. That is why an AI pipeline workflow is critical. It ensures data stays accurate, models follow strict rules, and every decision gets logged. Because of this, teams can detect fraud, assess risk, and approve transactions while staying compliant and audit-ready.
Healthcare
In healthcare, trust is everything. AI pipeline workflows help manage sensitive data carefully, validate model outputs, and monitor performance over time. As conditions change, pipelines support safe retraining so models do not fall behind. This makes AI more dependable for diagnosis support, patient monitoring, and operational planning.
Manufacturing
Meanwhile, manufacturers rely on constant data from machines, sensors, and supply chains. An AI pipeline workflow turns that stream into actionable insights. It helps predict equipment failures, improve quality checks, and reduce downtime. Over time, this leads to more efficient operations and fewer unexpected breakdowns.
Dealerships
In dealerships, timing matters. AI pipeline workflows help track customer behavior, service history, and inventory data in one place. Because everything stays connected and updated, dealerships can send reminders, predict maintenance needs, and offer better recommendations. This creates a smoother experience for both staff and customers.
Challenges and Considerations
Even with a solid AI pipeline workflow, challenges still exist. Building the pipeline is not always easy. It takes time, planning, and the right tools.
One common issue is data quality. If your data is incomplete or outdated, the entire pipeline suffers. As the saying goes, bad data leads to bad results. That is why strong validation and monitoring matter from day one.
Another challenge is complexity. As pipelines grow, they can become hard to manage. Too many tools, custom scripts, or manual steps can slow teams down. Therefore, simplicity and standardization should always be a priority.
Costs are also a factor. Training models, storing data, and running infrastructure can get expensive. Without careful monitoring, expenses can quietly grow over time.
Finally, governance cannot be ignored. AI systems must follow privacy laws, security standards, and ethical guidelines. Pipelines need built-in checks so compliance is automatic, not an afterthought.
Conclusion
AI is no longer just about building models. It is about running them reliably in the real world. That is exactly why an AI pipeline workflow matters.
A well-designed pipeline connects data, models, and business systems into one smooth process. It helps you move faster, reduce risk, and scale with confidence. More importantly, it turns AI from a one time project into a long-term capability.
As we move deeper into 2026 and beyond, organizations that invest in strong AI pipeline workflows will have a clear advantage. They will ship better models, earn more trust, and adapt faster to change. In the end, the pipeline is not just support for AI. It is the foundation that makes AI work.
FAQs
What is an AI pipeline workflow?
An AI pipeline workflow is a structured process that moves data through steps like preparation, training, deployment, and monitoring so AI systems work reliably over time.
How is an AI pipeline workflow different from AI automation?
AI automation focuses on automating tasks or decisions. An AI pipeline workflow focuses on building, managing, and maintaining the AI systems behind those decisions.
Do small teams need AI pipeline workflows?
Yes. Even small teams benefit from clear pipelines. Starting simple helps avoid problems later as systems grow.
What tools are used in AI pipeline workflows?
Common tools include data platforms, model training frameworks, orchestration tools, and monitoring systems. The exact tools depend on the use case.
Why are AI pipeline workflows important in 2026?
In 2026, AI systems run inside critical business workflows. Pipelines help keep models accurate, compliant, and trustworthy as data and conditions change.

